What Are Dental Veneers? Procedure, Pros, and Cons
Home » Dental crown
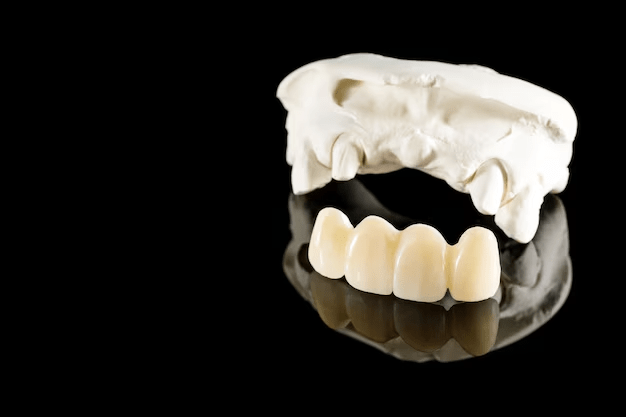

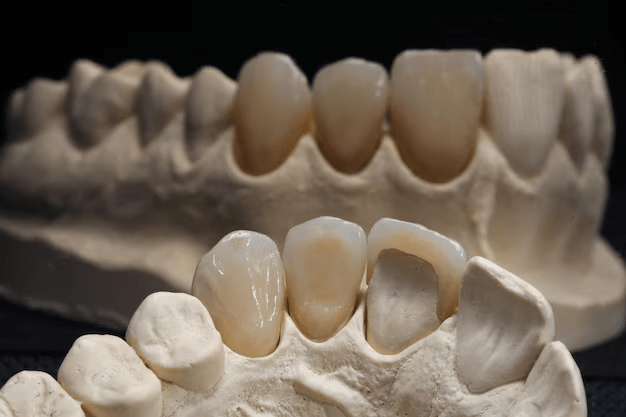
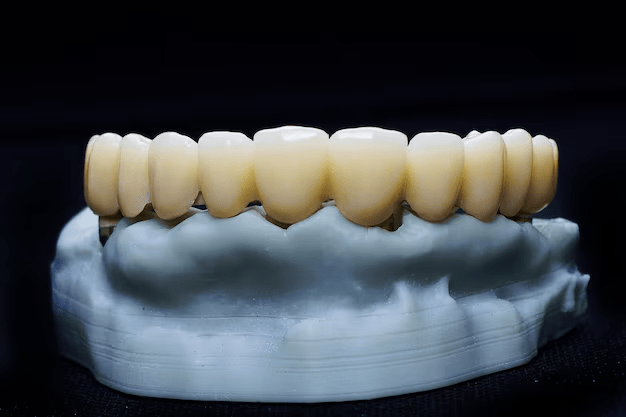
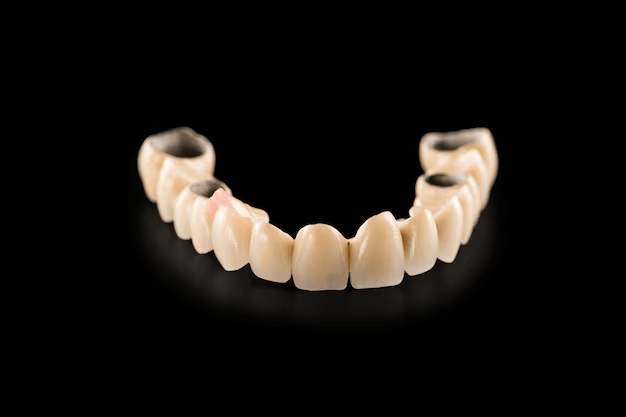
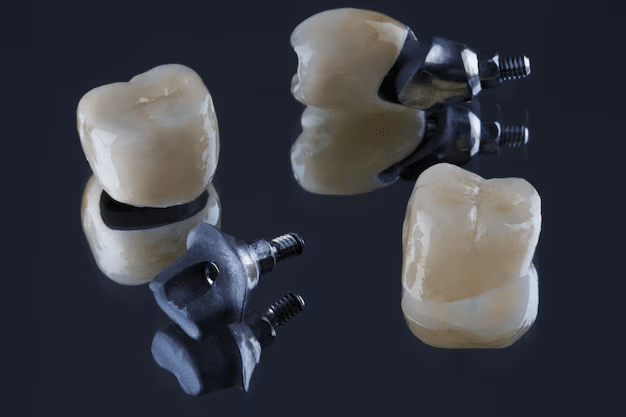
What are dental crown?
A dental crown fits over or “caps” a tooth or several teeth to remove any irregularities in the shape and size, making them stronger and better looking. Prosthetic crowns are fabricated using metal, porcelain bonded to a metal base, or new-generation all-ceramic materials. Fillings are ineffective when a tooth is comparatively weakened overall and a crown cannot be avoided. If a tooth is cracked, a crown keeps the tooth together to close the crack so the damage does not progress any further. This is also used when there is not enough of the actual tooth standing to hold a large filling in place, join a bridge, provide a defense for teeth that might be brittle, repair split teeth, conceal misshapen or stained teeth, or shield a tooth that has been treated with a root canal but is not strong enough.
How is a crown placed?
The tooth itself is anesthetized so that the dental crown may be prepped for placement by first removing any decaying or otherwise compromised substance. The remaining tooth structure is then cut, shaved, and contoured to the design of proper crown preparations. If needed, a restoring material is placed in the remaining tooth structure, commonly a composite resin, in preparation for a good foundation for the prosthetic dental crown. This procedure is named a “build-up.” Following preparation of the tooth, an impression of the teeth and gums is taken and a record sent to the lab for the crown. During the next appointment, the permanent cement is used to set the crown onto the teeth.
Will it look natural?
Yes. our main goal is to create crowns that look like natural teeth. That is why we take an impression. To achieve a certain look, a number of factors are considered, such as the color, bite, shape, and length of your natural teeth. Any one of these factors alone can affect your appearance. If you have a certain cosmetic look in mind for your crown, discuss it with us at your initial visit. When the procedure is complete, your teeth will not only be stronger, but they may be more attractive.
What is the difference between a cap and a dental crown?
There is no difference between a cap and a dental crown.
How long do crowns last?
To prevent damaging or fracturing the crowns, avoid chewing hard foods, ice or other hard objects. You also want to avoid teeth grinding. Besides brushing twice a day, cleaning between your teeth is vital with crowns. Floss or interdental cleaners (specially shaped brushes and sticks) are important tools to remove plaque from the crown area where the gum meets the tooth. Plaque in that area can cause dental decay and gum disease. Regularly scheduled examinations and hygiene appointments must be adhered to, or the same bacterial assault which causes decay and makes dental care necessary may cause the restorations to fail.
BRIDGES: FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is a bridge?
If a patient is edentulous and has a healthy attitude towards his oral condition and wants to keep hygiene practices in order, then he is an ideal candidate for a bridge. A bridge is by far the most appropriate solution for completing the organism’s deficit in the case of missing teeth. Should not be restored; this space leads to shifting of other teeth in that region, and teeth and gums will have increased risks of developing more cavities and gum diseases that lead to more tooth loss. Besides remodeling an altered bite and enhancing the ability to chew and speak fluently, bridges also preserve the aesthetic need by preventing sagging of facial structure that otherwise results in premature lines of ageing.
Who should get a bridge?
A bridge is suitable for a person with missing teeth, provided that the person is dedicated to practicing proper oral hygiene. An ideal suited to replace the space created by missing teeth in the mouth is a bridge. When left empty, it creates a gap that makes the other teeth shift, and it will make the teeth and gums vulnerable to decay and gum disease that leads to more tooth loss. Besides, not only bridges restore the abnormal occlusion, increase the capacity for chewing, as well as speech, and also preserve the appearance, preventing the deterioration of the face and formation of early wrinkles and age lines due to the collapse of the arch.
What type of bridges are there?
A cantilever bridge may be used if there are teeth on only one side of the span. This involves anchoring the pontic to one side over one or more natural, adjacent teeth. If there are no adjacent teeth to act as anchors, an implant is recommended—a metal post that is surgically embedded into the bone and capped with a crown as an abutment. In some cases where the span is large, a removable partial denture is recommended or even an implant-supported prosthesis.
What is the procedure of its fabrication?
For a traditional fixed bridge, the first appointment consists of reducing the adjacent abutment teeth that will act as anchors. Impressions are made, from which a metal framework, including the pontic, is created. By the second appointment, the final bridge is fitted over the teeth. The total treatment time is usually around one week, depending on the type of bridge. However, because it is often difficult to match the natural shade of your teeth, the treatment time may be longer.
How do I care for a bridge?
With a bridge, it is more important than ever to brush, floss and see a dental professional regularly. If buildup of food debris and plaque—the sticky film of bacteria formed from food acids—is not controlled, the teeth and gums can become infected, requiring further treatment and resulting in possible loss of the bridge. We recommend using floss threaders that help remove bacteria from hard-to-reach spaces between the bridge and adjacent teeth and gums. Crowns on the bridge cover most of the exposed portion of your tooth and decay does not affect a bridge since it is made of metal and /or porcelain. However, where the natural tooth meets the crown of the bridge can become decayed. If optimal oral hygiene care is maintained, a bridge can last for many years.
Suggestions and precautions
- Adjustment period: It is ok for the bridge to feel a little out of place for a few days after cementing. This is because the teeth around this area are adjusting to new forces both in between the teeth and upon biting.
- Preventive Procedures: To provide optimum longevity for your restorations and to prevent future decay and supporting-tissue breakdown, please use the following home care tips:
- Brush after eating and before bedtime around the bridge with a soft toothbrush, especially where the crown or bridge meets the gum line (margin). At this margin area harmful bacteria can be harbored to cause decay and gum disease. An electric toothbrush is highly recommended over manual to help you keep this area clean.
- Water Pik™ can be used with an antibacterial, alcohol free mouthwash at the gum line and under the bridge to keep this area healthy.
- Fluoride rinse is to be used before bed. Swish the fluoride rinse vigorously in your mouth for at least one minute. Do not swallow any of the rinse and do not eat or drink anything for 30 minutes.
- Use a proxybrush (interdental brush) to clean around the area after each meal
Chewing:
Do not chew hard foods on the restorations for 24 hours from the time they were cemented — to attain optimum strength, the cement must mature for approximately 24 hours Also avoid eating or chewing on hard objects, food or ice
Limit snacks; if high in sugar, brush this area or swish with water
Sensitivity :
Do not worry about mild sensitivity to hot or cold foods. This sensitivity will disappear gradually over a few weeks. Infrequently, sensitivity last longer than six weeks.
Recare: Inadequate return for examination is the most significant reason for prostheses failure. Visit us at regular six-month examination periods. Often problems that are developing around the restorations can be found at an early stage where they can be corrected easily and will be more affordable. Waiting for a longer time may require re-doing the entire restoration.
Problems:
Call us immediately if any one of these conditions occurs: If the tooth is the first tooth to hit when you bite down after a couple of days, contact us for an adjustment; a feeling of movement or looseness in the restoration; sensitivity to sweet foods; a peculiar taste from the restoration site; breakage of a piece of material from the restoration or sensitivity to pressure.
- Bindra Dental Clinic and Implant Center
- 0161 230 0101
- B Block, 74B, DMC Rd, near Dhami hospital, D-Block, Kitchlu Nagar, Ludhiana, Punjab 141001
- bindradentalclinic@gmail.com
